Smart cities embrace the wind of change
In the ongoing pursuit of sustainability, urban environments find themselves at the forefront of innovation. With the imperative to reduce carbon emissions and enhance energy efficiency, cities worldwide are turning to transformative technologies to revolutionise their energy landscapes. Here, Vijay Madlani, CEO of Katrick Technologies, an innovator in greentech solutions, explains the vital role modular renewable technologies can play in powering smarter, more sustainable cities.
According to the United Nations Human Settlements Programme, UN-Habitat, cities consume about 75 per cent of global primary energy and emit between 50 to 80 per cent of the world’s total greenhouse gas — despite covering less than two per cent of the world’s surface.
Smart cities could wield a significant influence in shaping global sustainability efforts. According to analytics by GlobalData, the smart cities market was valued at $262.5 billion in 2023, and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.2 per cent by 2027, which would put its value at around $698 billion. Smart cities use technologies including the Internet of Things (IoT) to improve citizen’s quality of life and their safety. With examples including Amsterdam in the Netherlands, New York, USA, and Seoul, South Korea, smart cities use new innovations and data analysis to benefit sustainability.
In its The State of European Smart Cities report, the European Commission (EC) agrees that “digitalisation, artificial intelligence (AI)-based solutions, and digital twins will play a significant role in speeding up the transformation towards carbon neutrality in European cities.” But the true value of smart cities lies in how technologies are used to minimise environmental impact.
Smart cities can become greener through various initiatives such as optimising power usage, creating walkable areas, improving public transportation, and implementing waste sensors using IoT technology. These efforts not only enhance sustainability but also improve the quality of life for residents. Furthermore, integrating green technologies and renewable energy sources into smart city infrastructure — like solar and wind — can significantly contribute to environmental preservation and reduce carbon emissions. Let’s look at some examples.
The quest for sustainability
Smart cities across Europe are increasingly adopting renewable energy sources in their energy infrastructure. These changes are catalysed by initiatives like the RePowerEU Plan, a strategy devised by the EU in response to recent global developments, particularly the Russian invasion of Ukraine and its weaponisation of the energy sector. The plan aims to accelerate the energy transition in Europe by addressing several key objectives, including speeding up energy efficiency, mitigating the use of fossil fuels, and reducing carbon emissions.
Innovative new technologies and flexible solutions will be key in achieving these objectives, but traditional technologies such as solar and wind farms require large amounts of open space and abundant natural resources — something that isn’t always easy to come by in cities which are often built up and unsuitable for capturing sufficient sunlight or laminar winds.
To address this and bring renewable power supply closer to the heart of smart cities, thinking outside the box and creating new modular technologies able to work around the constraints of cities will be key. Versatile alternatives to full-scale renewable installations offer a cost-effective, scalable, and efficient means of harnessing clean energy in urban environments. The adoption of modular power generation holds many benefits for smart cities; environmental, economic, and social.
Modular wind technology
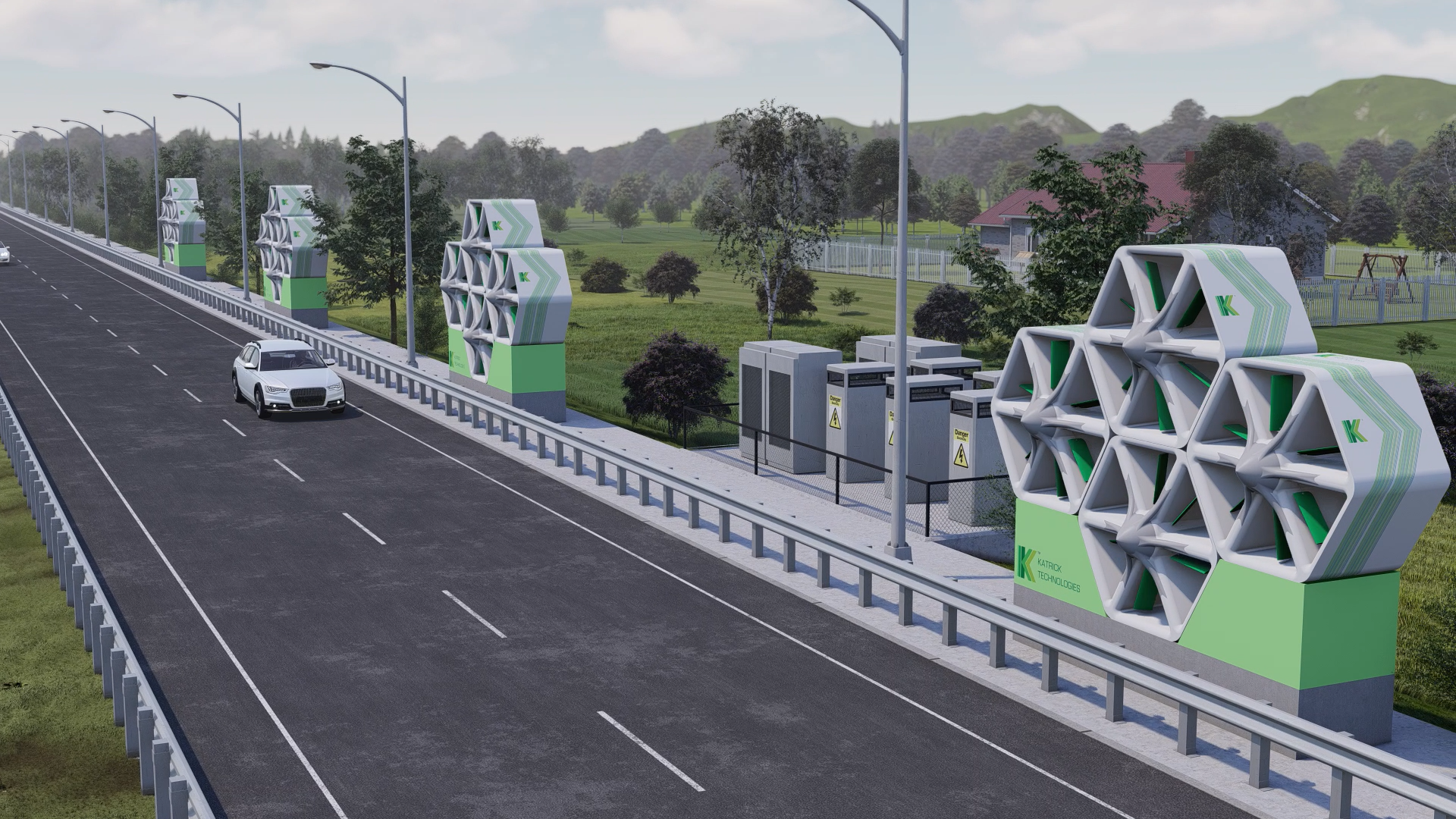
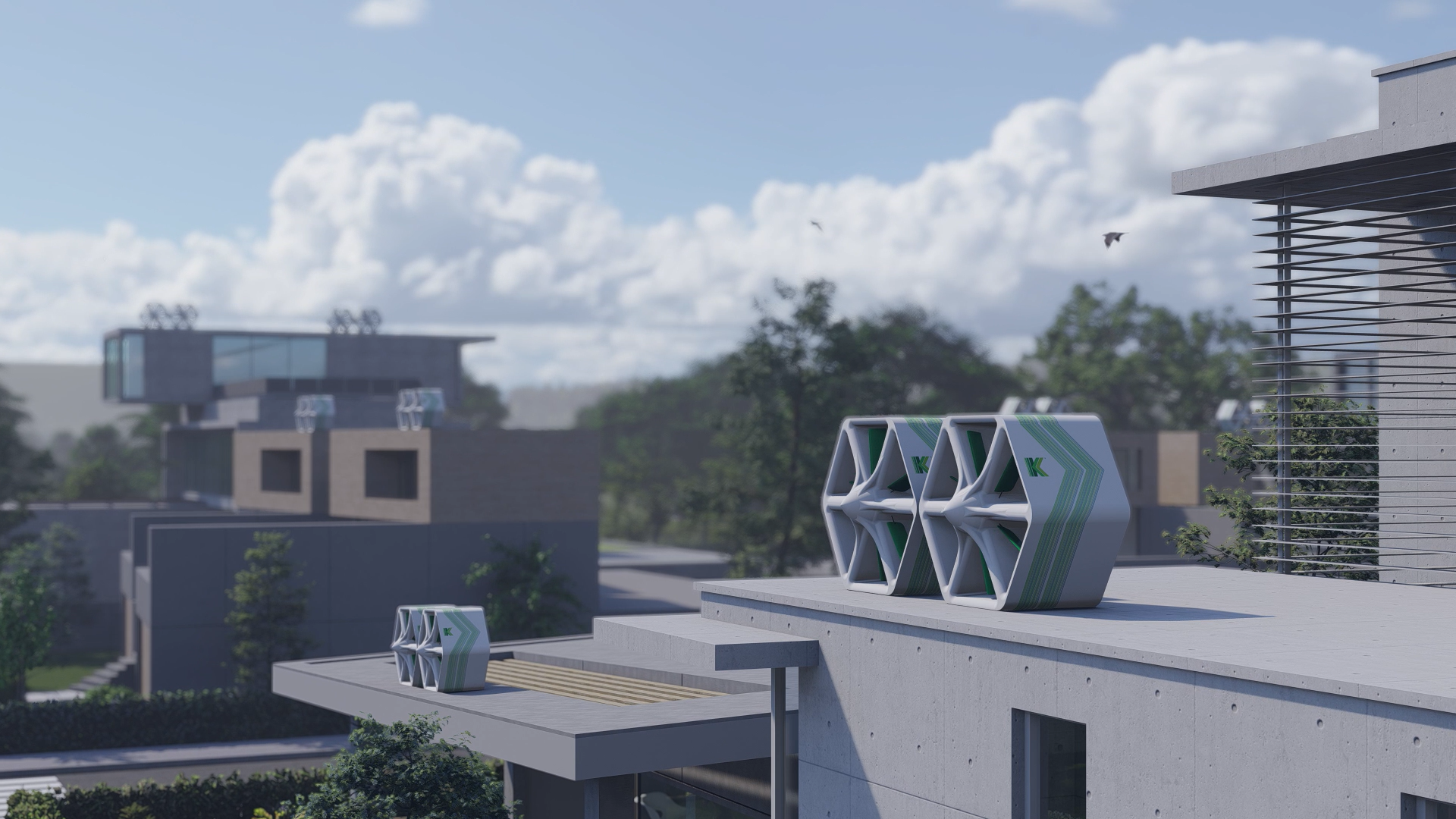
Wind technology is one of the most common forms of renewable energy, but wind turbines can only capture laminar winds at higher levels, making them unsuitable for use in most urban areas. However, unlike conventional wind turbines, modular solutions can offer a versatile and aesthetically pleasing solution. This is where innovative developments such as Katrick Technologies’ groundbreaking Wind Panel come in.
The Wind Panel represents a new advancement in renewable energy technology, offering innovative solutions tailored to the unique challenges faced by smart cities. These modular panels are designed to harness the power of wind energy in urban environments, in smaller spaces. They can be installed easily into urban infrastructure — building facades, rooftops, and street furniture — without necessitating extensive land use or structural modifications. This inherent flexibility not only minimises deployment costs but can also enhance the visual appeal of urban landscapes.
At the heart of Katrick Technologies' Wind Panel lies a sophisticated aerodynamic design that maximises energy capture efficiency even in the turbulent airflow patterns often found in urban environments. This cutting-edge design allows the panels to generate electricity from diverse wind frequencies including low-level ground winds, which makes them highly adaptable to the urban landscape. The result? Optimised and more efficient energy capture.
The decentralised nature of modular wind technologies can also help to ensure resilience against grid disruptions. Traditional power grids are vulnerable to disruptions caused by extreme weather events, equipment failures or cyber-attacks. When a centralised power plant fails, it can lead to widespread blackouts affecting large areas. Instead, modular wind power technologies can help foster local energy autonomy and make smart cities more resilient.
By reducing energy expenditure and enhancing energy efficiency, technologies such as Katrick Technologies’ Wind Panel offer substantial long-term cost savings for smart cities and their residents alike, paving a compelling pathway toward the realisation of smart, resilient, and sustainable cities.